2. Web Dynpro JAVA iViews
Before creating Web Dynpro JAVA iView you must have the following information ready with you:
- Web Dynpro JAVA Development Component (DC) name, if it is a local development then the component name.
- Application Name
Step-by-step process:
Steps 1 to Step 4 are same as in creation of Web Dynpro ABAP iView.
5. In the iView Wizard, select Web Dynpro for JAVA radio button and then press ‘Next’ button.
6. Select ‘Application Location’ as local and ‘iView type’ as ‘Web Dynpro iView per selected application’ and then press the ‘Next’ button.
7. Select the Web Dynpro Component and the Web Dynpro Application for which you want to create your iView and then click on the ‘Next’ button.
8. Click on ‘Finish’ button to complete the process. You have successfully created the iView for your Web Dynpro JAVA application, and now you can assign this Iview to pages, workset, roles and then to the user.
To test your newly created iView right click on the iView and then select ‘Preview’.
3. Business Server Pages (BSP) iViews
Before creating the BSP iView you must have the following information ready with you:
- System (Mandatory): Name of the Backend System
- Customer Namespace (Mandatory): SAP
- Application Namespace (Mandatory): SAP
- Application Name (Mandatory): Business Server Page (BSP) Application Name
- Start Page (Mandatory): Generally default.htm
- Application Parameters (Optional): If your application has any parameters then you can give them here.
Step-by-step process:
Steps 1 to Step 4 are same as in creation of Web Dynpro ABAP iView.
5. In the iView Wizard, select ‘iView template – Create an iView from an existing iView template’ radio button and then click on the ‘Next’ button.
6. Select the SAP BSP iView template and then click on ‘Next’ button.
7. Give a name and a unique Id to your iView and then press the ‘Next’ button.
8. Select Application as ‘BSP Definition Type’ and then click on the ‘Next’ button.
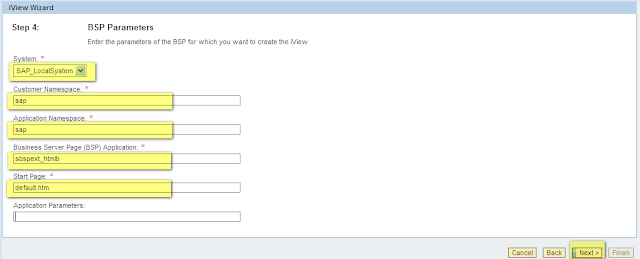
9. Select the System from the drop down list, enter SAP as the customer namespace, SAP as application namespace, BSP application name, start page and application parameters if there are any.
After entering all the information click on the ‘Next’ button.
10. Click on ‘Finish’ button to complete the process. So, you have successfully created the iView for your BSP application, and now you can assign this Iview to pages, workset, roles and then to the user.
To test your newly created iView right click on the iView and then select ‘Preview’.
4. SAP Transaction iViews
Before creating the SAP Transaction iView you must have the following information ready with you:
- System (Mandatory): Name of the Backend System
- Transaction Code (Mandatory)
Step-by-step process:
Steps 1 to Step 4 are same as in creation of Web Dynpro ABAP iView.
5. In the iView Wizard, select ‘iView template – Create an iView from an existing iView template’ radio button and then press ‘Next’ button.
6. Select the SAP Transaction iView template and then click on ‘Next’ button.
7. Give a name and a unique Id to your iView and then click on the ‘Next’ button.
8. Select SAP GUI for HTML as the GUI type and then press the ‘Next’ button.
10. Select the System from the drop down list, enter the Transaction Code and then press the ‘Next’ button.
11. Click on ‘Finish’ button to complete the process. So, you have successfully created the iView for your SAP Transaction, and now you can assign this Iview to pages, workset, roles and then to the user.
To test your newly created iView right click on the iView and the select ‘Preview’.
5. URL iViews
Before creating the URL iView you must have the following information ready with you:
• System (Mandatory): Name of the Backend System
• Transaction Code (Mandatory)
Step-by-step process:
Steps 1 to Step 4 are same as in creation of Web Dynpro ABAP iView.
5. In the iView Wizard, select ‘iView template – Create an iView from an existing iView template’ radio button and then press ‘Next’ button.
6. Select the URL iView template and then click on ‘Next’ button.
7. Give a name and a unique Id to your iView and then press the ‘Next’ button.
8. Give URL that provides content to your iView at runtime, and then press the ‘Next’ button.
9. Click on ‘Finish’ button to complete the process. So, you have successfully created the iView for your URL, and now you can assign this iView to pages, workset, roles and then to the user.
To test your newly created iView right click on the iView and the select ‘Preview’.