SAP BASIS ADMIN Roles & Responsibilities
I ) Administration includes user admin, Client admin, and backup in SAP environments.
.
II) Maintenance includes monitoring the servers, background jobs, system performance and avoiding bottlenecks in SAP environments.
Which process first connects to the database?
Application Server is just a dialog instance.
Central Instance is Dialog instance + Database Instance
What is the difference between clients 000 and 001?
Client 000 is the SAP source client, client 001 exists only on certain installations (e. g. solution Manager).
What is the difference between Sap lock and database lock?
A “SAP lock” is named “enqueue lock”, the enqueue is on a much higher level, e. g. a complete sales document is locked there whereas in the datbase usually only row locks exist. Since SAP runs on more database than Oracle (thanx god) one needed to have a mechanism, that is database independent and on a higher level.
What is Access method?
Access method is the way the output device is connected to SAP system. The access method is specified during the definition
What is the difference between ST02 and ST04 transaction monitoring?
ST02 is used only to monitor the memory related parameters like (buffer hit ratio, roll area, page area ) which in case on fulfilment will effect the performance of SAP.
ST04 we can completely do the database related monitoring like backup schedules, locks etc.
How to start & stop SAP Instance
Tablespace Coalesce
- He should be able to do user administration like creating and deleting users, assigning and resetting passwords, locking and unlocking users.
- He should be able to troubleshoot security or authorization problems using SU53, ST01 and SUIM
- He should be able to create roles using different methods like transactions, direct objects, missing authorizations, restrictions…etc
- He should be able to analyze and fix missing authorizations
- He should be able to do client administration like local client copies, remote client copy, create and deleting clients.
- He should be able to create and restore data backups
- He should be able to do printer or spool configuration and administration
- He should be able to manage the database space allocation
- How to Copying the one user
Use transaction SU01 or, from the System Administration Assistant Running Your Display Tasks (transactionSSAA), choose Entire view. SAP System Administration à Additional Administration Tasks System Users: Copying a User.
In transaction SU01, enter ADMIN##, choose Copy, then enter the name BASIS##. Deselect Authorization profiles and Activity groups. Enter a new password for BASIS## twice and save. - What is the total number of clients supported per SAP system?
- It’s from 000 to 999. Total 1000 clients are supported per SAP System.
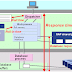
User
Admin(User Roles, Profiles, Activity
Groups and Authorizations)
|
Client
Admin
|
Backup
|
SU01- User Maintenance( Create new user, delete ,lock,Copy
Users)
SU01D-User
Display
SU02- Maintain
Authorization Profiles
SU03
- Maintain Authorizations
SU05-Maintain
Internet users
SU10
- User Mass Maintenance/locks
SMLG
- Maintain Logon Group
SUPC -Profiles
for activity groups
SUIM- Info system Authorizations, roles comparison
PFCG-Profile Generator(Activity Group Maintenance)
PFUD
- User Master Data Reconciliation
SM19 -Security Audit Configuration(Trace a User’s
Activity)
SSAA/SU01 -Copying the one user
To
disable multiple user logins within the same client implement this parameter
in the instance profile
login/disable_multi_gui_login
= 1
Availability of SAP Instance & Application:
SM52,SM21,SRZL,
SM50, SM04, SM12, SM13, ST22, SM37, and SP01.
Table Maintenance ( use SA38 or Choose system service)
· To copy tables across clients, invoke RSCLTCOP
· To make table adjustments across clients, RSAVGL00
· To invoke the Substitution/Validation utility,
invoke RGUGBR00
· To transport SAP script files across systems, RSTXSCRP
· To release batch-input sessions automatically.RSBDCSUB
· RSMI3001 –
deleting cancelled Update Records
· RSPO0041 –
Obsolete spool Objects
· RSPO0043 –
Spool lists Which are remnants of cancelled by job
· RSUSR003 Check
the passwords of users SAP* and DDIC in all clients
· RSUSR006 List
users last login
List
of inactive users logs –
se38-RSUSR200
Incorrect
SAP login logs –RSUSR006
|
SCC3-
Checking Client Copy Log
SCC4-Client
Administration( New client Creation)
SCC5-Client
Delete
SCC7-Client
Import Post-Processing
SCC8-
Client Export
SCCL-
Local Client Copy with in the same system
SCC9-Remote
client copy( Copying the clients and system)
How to Lock / Unlock a Client
To
lock or unlock a client in R/3 System, run the following function modules in
: transaction se37
SCCR_LOCK_CLIENT
( to lock the client)
SCCR_UNLOCK_CLIENT
(to unlock the client)
Locked Information
SM01
- lock/unlock transaction
SU01
-User accountslocked/unlocked (USR02 table ,uflage is
64-locked -> uflag is 0 unlocked )
How do you Lock/Unlock user in SAP?
SQL>
UPDATE USR02 SET UFLAG = '64' where BNAME=’USERID’ AND MANDT=’CLIENT’
SQL>
COMMIT
To
unlock an user use
SQL>
UPDATE USR02 SET UFLAG = '0' where BNAME=’USERID’ AND MANDT=’CLIENT’
SQL>
COMMIT
View
Locked Transactions- SM01 (You need to look in field
CINFO, table TSTC, you can use either SE11 or SE16 to browse the
table contents )
SM12-
Old lock entries
TO
Lock/Unlock a Client to Prevent Logons-
-
tp locksys <SID> pf=tpprofile
-
tp unlocksys <SID> pf=tpprofile"
Scheduling of system maintenance jobs
· RSBTCDEL Clean
the old background job records
· RSDBCREO Clean
batch input session log
· RSPO0041 Removing
old spooling objects
· RSSNAPDL Clean
the old ABAP error dumps
|
· Brtools & Database (EXP/IMP)
Brtools
login:
cd
d:\usr\sap\ser\sys\exe\run
set
sapdata_home=d:\oracle\ser
set
oracle_sid=ser
brtools
Brtools –v à to
check brtools version
Brspace –f tbexport –t user02
Brtools – db backup
Brconnect –u / -c –f cleanup
Brbackup –u/-c force –t online –m all –p
initser.sap -w use_dbv
-v
D:\backup
Brconnect -u/-c –f stats –t oradic_stats
Brbackup –u /
Brconnect –u/-c –f stats –t all –f collect
· DB12 SAP Backup Logs
Spool Management
SP01-
Spool Output Cotroller
SP11- TemSe
directory
SP12- TemSe
Administration
SPAD-
Spool Administration
Database
Administration
AL02 Oracle
DB Monitor
DB01 Analyze
exclusive lockwaits
DB02 Analyze
tables and indexes
DB13 Planning
Calendar
DB15 Data
Archiving: Database Tables
SM31 Table
maintenance (viewing and download tables)
DB14 Database
Monitor
Dbacockpit-
ST04 Database
alert logs and Perform.
Check the work Process-SM50
Ps
–elf | grep | grep dw
Ps
–elf | grep | grep ms
Ps
–elf | grep | grep sapos
How
to Kill work process in SAP?
SM50
,SM04 Or Kill -9
How
to find Long Running SAP JobsSM37,ST05,STAT,STAD
OR ST30
If
you have a long running Job, how do you analyse?
You
can analyze the long running job using transaction SE30
|
.
II) Maintenance includes monitoring the servers, background jobs, system performance and avoiding bottlenecks in SAP environments.
- He should be able to monitor and manage the servers, background jobs, performacne of the system
- He should be able to monitor the status of work processes, application servers and system logs etc…
- He should be able to rectify any type of problem related to operating systems
- He should be able to configure SAP GUI at client computers
- He should be able to rectify minor networking problems
- He should have through understanding of IP address configurations and pinging concept
- He must able to troubleshoot any client or server problems
- He should be able to create RFCs and should be able to configure TMS (Transport Management System)
Monitoring the servers/System
|
Background jobs
|
AL08 Current Active Users
AL18 OS filesystem alert ( df-k | more)
OS01 LAN check with ping
RZ01 Job Scheduling Monitor
RZ03 Presentation, Control SAP Instances
RZ08 SAP alert Monitor
RZ10 Maintenance of Sap profile Parameter
ST01 System Trace
ST02 Setups/Tune Buffers
ST04 Select DB activities
ST05 Performance trace
ST06 Operating System Monitor, ideal for analyzing the performance of the entire SAP technology stack.
ST07- useful in reviewing end users logged into the entire system
ST10 Table call statistics
ST03 /ST03N Performance, SAP Statistics, Workload Monitor
ST07 Application monitor
STAT Local transaction statistics
STUN- Performance Monitoring
SM51- SAP System Log
CCMS - System Monitoring (RZ20)
SSAA- useful in conducting routine daily, weekly, and monthly systems administration functions
SMLG- to monitor how well SAP's logon load balancing is performing; use F5 to drill down into group-specific performance data
SM66- ideal for looking at system-wide
performance relative to processes executing on every application and batch server within an SAP system
SM12- SAP system log
ST22- to review ABAP dumps and therefore identify program errors (to aid in escalating such issues to the responsible programming team)
|
SM36 Background Job Scheduling
SM37 Background Job Monitoring
SM39 Job Analysis
SM49 Execute External OS commands
SM62 Maintain Events
SM64 Release of an Event
SM65 Background Processing Analysis Tool
SM69 Maintain External OS Commands
Job scheduling Stages:
Scheduled, Released, Active, Finished ,Cancelled
Transport Management System
STMS Transport Management System
SE01 Transport and Correction System
SE06 Set Up Workbench Organizer
SE07 CTS Status Display
SE09 Workbench Organizer
SE10 Customizing Organizer
SE11 ABAP/4 Dictionary Maintenance
SE16 Data Browser
SE80 Repository Browser
SM30 Call View Maintenance
SM31 Table Maintenance
SCC1 Client Copy - Special Selection
STMS Transport Management System
|
III ) Perform day to day BASIS admin responsibilities including troubleshooting, analyze load , alert monitor and Configuration
Monitoring
|
Alert Monitoring
| |
AL08 Current Active Users
OS01 LAN check with ping RZ01 Job Scheduling Monitor RZ03 Presentation, Control SAP Instances ST01 System Trace ST02 Setups/Tune Buffers ST04 Select DB activities ST05 Performance trace ST06 Operating System Monitor ST10 Table call statistics ST03 Performance, SAP Statistics, Workload ST07 Application monitor STAT Local transaction statistics STUN Performance Monitoring (not available in R/3 4.6x) |
AL01 SAP Alert Monitor
AL02 Database alert monitor
AL04 Monitor call distribution
AL05 Monitor current workload
AL16 Local Alert Monitor for Operat.Syst.
AL18 Local File System Monitor
RZ20 CCMS Monitoring
Configuration
FILE Cross-Client File Names/Paths
RZ04 Maintain Operation Modes and Instances
RZ10 Maintenance of Profile Parameters
RZ11 Profile parameter maintenance
SE93 Maintain Transaction Codes
SM63 Display/Maintain Operating Mode Sets
SPRO Customizing: Initial Screen
SWU3 Consistency check: Customizing
|
IV ) Important Parameters & Tables
Profile Parameters for Client Login and password security (RZ10, RZ11)
|
Important Tables
|
login/accept_sso2_ticket
login/certificate_request_ca_url
login/certificate_request_subject
login/create_sso2_ticket
login/disable_cpic
login/disable_multi_gui_login
login/disable_multi_rfc_login
login/disable_password_logon
login/failed_user_auto_unlock
login/fails_to_session_end
login/fails_to_user_lock
login/min_password_diff
login/min_password_digits
login/min_password_letters
login/min_password_lng
login/min_password_specials
login/no_automatic_user_sapstar
login/password_change_for_SSO
login/password_expiration_time
login/password_logon_usergroup
login/password_max_new_valid
login/password_max_reset_valid
login/system_client
login/ticket_expiration_time
login/ticket_only_by_https
login/ticket_only_to_host
login/ticketcache_entries_max
login/ticketcache_off
login/update_logon_timestamp
|
To find an Instance Name SVERS
To find OS platform TSLE4
Check Table Space RSORAT01
Check Table Extent RSORATC5
User administration
User master USR01
Logon data USR02
User address data USR03
User master authorizations USR04
User Master Texts for Profiles (USR10) USR11
User master: Authorizations UST12
User master authorization values USR12
Short Texts for Authorizations USR13
Prohibited passwords USR40
Objects TOBJ
Authorization Object Classes TOBC
Profile Name for Activity Group TPRPROF
Table for development user DEVACCESS
Batch input queue
DATA DEFINITION Queue APQD
Queue info definition APQI
Job processing
Job status overview table TBTCO
Batch job step overview TBTCP
Spool
Spool: Print requests TSP02
Runtime errors
Runtime errors SNAP
Message control
Processing programs for output TNAPR
Message status NAST
Printer determination NACH
SBAT : BASIS System Tables TSTCT : Transaction Code Texts
|
V) Daily monitoring Tcodes & TOP SAP BASIS CRITICAL ADMINISTRATIVE TASK
Daily monitoring Tcodes
|
Top SAP BASIS Critical Admin Task
|
AL08 Current Active Users
SM12 Display and Delete Locks( lock entries)
SM13 Display Update Records( Check the Pending Updates)
SM21 To check the System Logs
SM50 Work Process Overview
SM51 List of SAP Servers
SM66 System Wide Work Process Overview
ST22 To Check ABAP Dump /4 Runtime Error Analysis
ST01 System Trace
ST02 Setups/Tune Buffers
ST03N Workload overview
ST04 Select DB activities( Database Performance Analysis)
ST05 Performance trace
ST06 Operating System Monitor
ST10 Table call statistics
ST03 Performance, SAP Statistics, Workload
SU56 Analyze User Buffer
OS01 LAN check with ping
RZ01 Job Scheduling Monitor
RZ03 Presentation, Control SAP Instances
ST07 Application monitor
STAT Local transaction statistics
SM35 Display Batch Jobs
SP12 Deleting Obsolete Temporary Objects and Reclaiming the Space
DB2OLD Checks the TBS Growth size
SM37 /36 To Check the background status on previous day
DB13 To Assign the Backup schedule
PFCG Profile Generator( Role, Authorization)
|
1. SAP System R/3 System Status Check : Logon Test
2. Backup Management: DB12
3. Application Server Status Check: SM51
4. CCMS Alerts Check: RZ20
5. Work Process Status Check: SM51
6. Failed Updates Monitoring: SM13
7. System Log Review: SM21
8. Jobs Monitoring: SM37/SM35
9. Check for old locks SM12
10. Spool Administration SP01
11. Check for ABAP/Short dumps ST22
12. Work load Analysis: ST03/ST03N
13. Review buffer statistics ST02
14. Database Performance Analysis ST04
15. User Management SM04/AL08
16. Operating System Monitoring: OS06
17. SE38/SA38/SE16/SM30 – Sensitive T-Code
|
- Basis consultant should be able to handle the administration of sap including the installation, configuration and maintenance.
- Installation may include SAP R/3, ECC, Net weaver, Net Weaver components, Solution Manager etc..
- He should be able to do the sap license management( SLICENSE,SAPLICENSE –SHOW)
- He should be able to analyze the ABAP dumps
- He should be able to do system copies
SAP R/3 dispatcher and work processes
Types of work processes:
Message
|
Coordinates the communication between different instances of a single SAP R/3 system. Used for Logon purpose and load balancing
|
Dispatcher
|
Redirect the request from GUI client to free process
|
Dialog
|
Interpreting the ABAP code and execute the business logic. Used for interactive online processing
|
Batch
|
For Background jobs
|
Enqueue
|
Single “Central Lock Management Service” that controls the locking mechanism between the different application servers and the database.
|
Update
|
Responsible for consistency in asynchronous data changes.
|
Gateway
|
Used for transport of bigger amount of data between application servers as well as external (non SAP) systems that communicate with SAP
|
It’s a Message Server process that connects first to the database
Difference between Application server and Central Instance?Application Server is just a dialog instance.
Central Instance is Dialog instance + Database Instance
What is the difference between clients 000 and 001?
Client 000 is the SAP source client, client 001 exists only on certain installations (e. g. solution Manager).
What is the difference between Sap lock and database lock?
A “SAP lock” is named “enqueue lock”, the enqueue is on a much higher level, e. g. a complete sales document is locked there whereas in the datbase usually only row locks exist. Since SAP runs on more database than Oracle (thanx god) one needed to have a mechanism, that is database independent and on a higher level.
What is Access method?
Access method is the way the output device is connected to SAP system. The access method is specified during the definition
What is the difference between ST02 and ST04 transaction monitoring?
ST02 is used only to monitor the memory related parameters like (buffer hit ratio, roll area, page area ) which in case on fulfilment will effect the performance of SAP.
ST04 we can completely do the database related monitoring like backup schedules, locks etc.
How to start & stop SAP Instance
NT- Windows
|
UNIX
|
Startsap name=<sid> nr <system number> sapdiahost =<hostname>
|
Startsap db
Startsap r3
Or
Startsap all
|
Stopsap name=<sid> nr <system number> sapdiahost =<hostname>
|
Stopsap r3
Stopsap db
Or
Stopsap all
|
Before stopping SAP System
Check status of User/Active Process
List Of Users : SM04,AL08
List of Active Process : SM50,SM66
Send a system Message : Sm02
|
Or use CCMS ( RZ03) – Control- start& stop
|
Security Management (FAQ)
1. How to transport roles from Production to Development or Sandbox?
Goto PFCG and enter the role which you want to transfer to other system.
Goto utilities->Mass download it will ask the path where to download/save that role on local desktop give the location and save it.
Next logon to the system where you want that particular role. Go to PFCG-> Role -> upload.
Give the path where the role is saved. it accepts and generates successfully
2. How to check the missing authorisation for the user not having the option “su53″?
You can use Trace function, ST01, you can trace the user activity and from the log you can see the authorization missing.
Start an authorization trace using the ST01 transaction and carry out the transaction with a user who has full authorizations. On the basis of the trace, you can see which authorizations were checked.
3. What is the difference between role and a profile?
Role and profile go hand in hand. Profile is bought in by a role. Role is used as a template, where you can add T-codes, reports….. Profile is one which gives the user authorization. When you generate a role, a profile is automatically created.
4. What is the use of role templates?
User role templates are predefined activity groups in SAP consisting of transactions, reports and web addresses.
5. What is the difference between single role & composite role?
A role is a container that collects the transaction and generates the associated profile. A composite role is a container which can collect several different roles.
6. Is it possible to change role template? How?
Yes, we can change a user role template. There are exactly three ways in which we can work with user role templates
We can use it as they are delivered in sap
We can modify them as per our needs through pfcg
We can create them from scratch.
For all the above specified we have to use pfcg transaction to maintain them.
Please explain the personalization tab within a role.
Personalization is a way to save information that could be common to users, I meant to a user role… E.g. you can create SAP queries and manage authorizations by user groups. Now this information can be stored in the personalization tab of the role. (I supposed that it is a way for SAP to address his ambiguity of its concept of user group and roles: is “usergroup” a grouping of people sharing the same access or is it the role who is the grouping of people sharing the same access?)
7. How to insert missing authorization? Ways?
su53 is the best transaction with which we can find the missing authorizations.and we can insert those missing authorization through pfcg.
8. Someone has deleted users in our system, and I am eager to find out who. Is there a table where this is logged?
Debug or use RSUSR100 to find the info.
Run transaction SUIM and down its Change documents.
9. How can i do a mass delete of the roles without deleting the new roles?
There is a SAP delivered report that you can copy, remove the system type check and run. To do a landscape with delete, enter the roles to be deleted in a transport, run the delete program or manually delete and then release the transport and import them into all clients and systems.
It is called: AGR_DELETE_ALL_ACTIVITY_GROUPS.
To used it, you need to tweak/debug & replace the code as it has a check that ensure it is deleting SAP delivered roles only. Once you get past that little bit, it works well.
10. How to compare the roles where created or defined in two different systems?
For role comparison both the roles must be in the same system, in same client
Transaction code SUIM -> Comparison-> Roles
If the roles are in different system, then transport the role into one of the system and do comparison. If no transport connection defined then, you can use the upload and download option in the PFCG
Steps for Role Comparing:
1. Run the t-code SUIM
2. Go To Comparison and select the option of roles
3. Click on Across systems option it will give option to select the sys name under Remote Comparison there enter the SYS ID between which system you want to do comparison and put the role name in compare role section then execute it will give you the result.
4. If there is any difference between the t-codes it will b in red color otherwise in yellow.
11. What is the procedure for creating new user which have all features define under SAP* user and which could allow me to make the configurations?
Creating new user with superuser authorizations.
1. Goto SU01 –
username : sapuser
|–>Create.
2. In default settings, give
:Mr
first name : sap
last name : user
3. Goto next tab,
give initial password :1234
repeat password : 1234
4. Goto profiles.
type- sap_all (say enter)
sap_new (say enter)
Then save….
See the message in status bar, (user created successfully)
5. Login with the new user. change the password. now this user contains all superuser authorizations
12. The administrator user cannot be used to log on to the J2EE Engine because it has been locked. How will you correct the situation?
To correct this situation, I had to use an emergency user account.
SAP* user account has full administrator authorizations, but this account doesn’t have a default password. It must be specified when account is activated. Once SAP* is activated, no other user can log in to the system.
Check properties on Config Tool (Edit UME):
- ume.superadmin.activated (set ‘true’);
- ume.superadmin.password (specify a password).
Restart Application Server.
You have all users locked onto ABAP system. How will you deal with this situation?
Make sure your login/no_automatic_user_sapstar profile value is set to 1.
Log on to host system and connect to database.
Use the following query:
- delete sid.USR02 where BNAME=’SAP*’ and MANDT=’xxx’;
Now SAP* user is generated again with default password “pass”.
13. How would you copy all users from DEV to PRD?
Execute transaction SCC8 and select the profile SAP_USER. Then specify target system and schedule background job. This will export all users from the source system in the form of request.
Now login to the destination system and enter tcode SCC6. Specify the request number generated while exporting and click on “prepare import”.
You can check logs in SCC3 transaction.
select a.tablespace_name, a.file_id, a.block_id, a.blocks,
b.block_id
from dba_free_space a, dba_free_space b
where a.tablespace_name = 'SYSTEM'
and b.tablespace_name = 'SYSTEM'
and a.tablespace_name = b.tablespace_name
and a.file_id = b.file_id
and a.block_id+a.blocks = b.block_id
alter tablespace USERS coalesce;
Job profile for SAP BASIS Administrator
1.SAP Administration
1. Starting and Stopping SAP instance/(s)
2. User Administration – Setup & Maintenance
3. Authorization/Role/ Profiles – Setup & Maintenance
4. Setup SAP Security
5. Maintenance of System’s Health
6. Monitor System Performance and Logs
7. Spool and Print Administration
8. Maintain System Landscape
9. Transport Management Systems
10. Manage Change Requests
11. Create/Manage Batch Jobs
12. Backup Schedule,run & Monitor Backup of SAP
13. Apply Patches,Kernel & OSS Notes
2. Database Administration
1. Database Space Management
2. Database Backup
3. Database Recovery
4. Database log (Redo log, Archive Log) management
5. Database Performance Tunning
3. Operation System Administration
1. Operatin System Security
2. Operation System Performance Tunning
3. OS Space management
4. OS level background Job Management
5. OS level backup and recovery
4. Overall System Monitoring
1. Monitoring R3 Servers and Instances
2. Monitoring Users and Authorizations
3. Monitoring Security Part
4. Monitoring workload analysis
5. Monitoring Processes
6. Monitoring Buffers
7. Monitoring Operating system
8. Monitoring Database
9. Monitoring Backups
Recommended daily tasks
| |
Task
|
T-Code
|
| 1. Check whether the systems are up | |
| 2. Check whether the backups finished without errors | |
| 3. Check for alerts in CCMS monitors | |
| 4. Check for hanging or stopped work processes | |
| 5. Check system log for errors/warnings | |
| 6. Check whether any background jobs got canceled for any reason | |
| 7. Check the lock entry list | |
| 8. Look for any failed updates | |
| 9. Check for users logins from unknown terminals/locked users | |
| 10. Analyze program dumps | |
| 11. Check for excessive swaps and buffer statistics | |
| 12. Review Database performance | |
| 13. Check database for space critical objects | |
| 14. Check the average response times | |
| 15. Check for OS level alerts | |
| 16. Check CPU load and memory usage | |
| 17. Review SAPDBA calendar job logs | |
| 18. Check archive directory status | |
Recommended weekly tasks
| |
Task
|
T-Code
|
| 1. Check database for free space | |
| 2. Monitor tablespace growth | |
| 3. Monitor total DB growth | |
| 4. Clean up Spool | |
| 5. Clean up transport buffers | |
| 6. Run TemSe consistency check | |
| 7. Review security audit log | |
| 8. Check for adequate file system space | |
| 9. Analyze Early Watch reports | |
Recommended monthly tasks
| |
| 1. Cycle the R/3 system to defragment memory | |
| 2. Analyze the database growth and plan for storage | |
| 3. Review directory structure and need to move data files | |
| 4. Cleanup old logs | |
Recommended quarterly tasks
| |
| 1. User security overview | |
| 2. Review SAP profile parameters | |
| 3. Review the standard scheduled jobs | |
| 4. Test the backup by restoring | |
| 5. Archive the old transport files | |
| 6. Maintain SAPDBA and database parameter files | |
| 7. Review maintenance contracts for all hardware / software | |
| 8. Check for usage versus licensing | |
Recommended annual tasks
| |
| 1. Audit user security | |
| 2. Audit profiles and authorizations | |
| 3. Review user roles | |
| 4. Maintain activity groups/profiles | |
| 5. Cleanup clients in test/development systems | |
| 6. Check workbench organizer settings. | |
| 7. Refresh test system. | |
| 8. Simulate disaster recovery/failover testing | |
Software maintenance (as needed)
| |
| 1. Applying support packages | |
| 2. Applying database patches | |
| 3. Upgrading kernel | |
| 4. Change Management /applying notes | |
Additional services (as needed)
| |
| 1. User Maintenance / Profiles creation and maintenance | |
| 2. Printer definition maintenance | |
| 3. Data archiving | |
| 4. Technical Upgrades | |
| 5. Server Migration | |



Very good
ReplyDelete